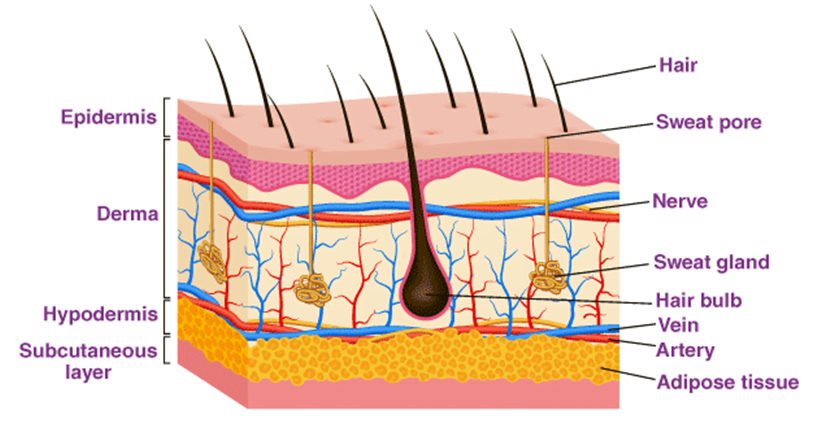
Human skin is the outer covering of the body, consisting of three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves several important functions, including protection from external harm, regulating body temperature, and sensory perception.
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin and is primarily composed of dead skin cells, called keratinocytes. The dermis is the middle layer and contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. The subcutaneous tissue is the deepest layer and contains fat cells and connective tissue.
The skin also contains several appendages, including hair follicles; sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. Hair follicles produce hair, while sweat glands produce sweat that helps regulate body temperature. Sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum, which helps moisturize and protect the skin.
The skin is exposed to a variety of environmental factors, including UV radiation, pollutants, and microorganisms, which can cause damage and lead to skin diseases. Proper care and protection of the skin, such as wearing sunscreen and avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, can help maintain its health and function.
Type of human skin
There are four main types of human skin:

- Normal skin: This type of skin is well-balanced, with a good balance of moisture and oil production. It is not too dry or too oily, and it has a smooth texture and even tone.
- Dry skin: Dry skin is characterized by a lack of moisture in the skin, which can cause flakiness, itching, and a tight feeling. People with dry skin may also be prone to wrinkles and fine lines.
- Oily skin: Oily skin is characterized by an overproduction of oil by the sebaceous glands, which can lead to shiny, greasy skin and an increased risk of acne.
- Combination skin: Combination skin is a mix of oily and dry skin, where some areas of the face (such as the T-zone, which includes the forehead, nose, and chin) are oily, while other areas (such as the cheeks) are dry.
It’s worth noting that these are general categories and not every individual’s skin falls perfectly into one of these types. Skin can also change over time due to factors like age, hormonal changes, and environmental factors.
Skin disease

There are numerous skin diseases that can affect human skin. Some of the most common skin diseases include:
- Acne: A skin condition that results from the clogging of hair follicles with oil and dead skin cells, causing pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads.
- Eczema: A group of skin conditions that cause inflammation, itching, and redness. It can be triggered by allergies, irritants, or stress.
- Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to build up rapidly, leading to thick, scaly patches of skin.
- Rosacea: A chronic skin condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels on the face, as well as acne-like bumps.
- Dermatitis: A general term used to describe inflammation of the skin, which can be caused by a variety of factors, such as irritants, allergies, or infection.
- Skin cancer: Abnormal growth of skin cells that can result in various types of cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
There are many other skin diseases that can affect human skin, and treatment will depend on the specific condition and its severity. It’s important to seek medical advice if you suspect you have a skin disease.
Causes of skin disease
There are several causes of skin disease, including:

- Genetics: Some skin diseases have a genetic component, meaning they are inherited from family members.
- Infection: Skin diseases can be caused by a variety of microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites.
- Allergies: Skin diseases can be triggered by an allergic reaction to a substance, such as certain foods, medications, or cosmetics.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental factors, such as sunlight, pollution, and chemicals, can cause or exacerbate certain skin diseases.
- Hormonal changes: Changes in hormones, such as during puberty or pregnancy, can lead to changes in the skin and trigger skin diseases.
- Immune system disorders: Skin diseases can be caused by autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
- Trauma: Skin diseases can be caused by physical trauma to the skin, such as burns, cuts, and scars.
It’s important to identify the cause of a skin disease in order to properly treat it. In many cases, a combination of factors may be contributing to the disease. Seeking medical advice is often the best course of action.
Symptom of skin disease
The symptoms of skin diseases can vary widely depending on the specific condition. Some common symptoms of skin diseases include:
- Rash or redness on the skin
- Itching, burning or stinging sensation
- Dry or flaky skin
- Blisters or lesions on the skin
- Scaling or thickening of the skin
- Swelling or inflammation
- Changes in skin colour or texture
- Pain or discomfort
- Oozing or discharge from the skin
- Ulcerations or open sores.
It is important to note that many skin diseases have similar symptoms, so a proper diagnosis from a medical professional is necessary to determine the specific condition and provide appropriate treatment. If you notice any changes in your skin or experience any of these symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical advice.
Treatment of skin disease by medicine
The treatment of skin diseases by medicine depends on the specific condition and its severity. Some common treatments for skin diseases include:
- Topical medications: These are medications applied directly to the skin, such as creams, ointments, and lotions. Topical medications can help relieve symptoms and treat the underlying condition.
- Oral medications: Some skin diseases may require oral medications, such as antibiotics, antifungals, or steroids. These medications are ingested and work from within the body to treat the condition.
- Light therapy: Some skin diseases can be treated with light therapy, which involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light to help reduce inflammation and other symptoms.
- Immunomodulators: Certain skin diseases can be treated with immunomodulators, which help to modify the immune response and reduce inflammation in the skin.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove cancerous or pre-cancerous skin cells or to remove lesions that are causing discomfort or affecting quality of life.
It is important to follow the advice of a medical professional when treating skin diseases with medication. Some medications can have side effects or interact with other medications, so it’s important to disclose all medications and medical conditions to your doctor. Additionally, proper skin care and lifestyle changes may also be recommended to help manage skin diseases.
List of medicine use in treatment of skin disease
There are many medicines that can be used to treat various skin diseases, including:
- Topical corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory medications that can be used to treat eczema, psoriasis, and other skin conditions.
- Antihistamines: These medications can help relieve itching and inflammation caused by allergies, hives, and other skin conditions.
- Antifungal medications: These medications can be used to treat fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and nail fungus.
- Antibiotics: These medications can be used to treat bacterial infections of the skin, such as impetigo, cellulitis, and acne.
- Retinoids: These medications are derived from Vitamin A and can be used to treat acne, psoriasis, and other skin conditions.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications can be used to treat autoimmune skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema.
- Light therapy: This involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light to help reduce inflammation and other symptoms of various skin diseases.
- Moisturizers: These can be used to relieve dry skin and help manage conditions such as eczema.
It is important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and the medication prescribed will depend on the specific condition and individual needs of the patient. It is important to consult with a medical professional before using any medication to treat a skin condition.
Nutraceuticals treatment and prevention of skin disease
Nutraceuticals are food products that have medicinal or health benefits beyond their nutritional value. There are several nutraceuticals that have been studied for their potential to prevent and treat skin diseases. Here are a few examples:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats found in fish, nuts, and seeds have anti-inflammatory properties and may help improve skin health, particularly in conditions such as psoriasis and eczema.
- Probiotics: These are “good” bacteria that can be found in fermented foods and supplements. Studies suggest that probiotics may help improve skin conditions such as acne and rosacea.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is important for skin health and can be obtained through sun exposure, diet, and supplements. Studies have found that vitamin D may be helpful in treating skin conditions such as psoriasis.
- Zinc: This mineral is important for immune function and skin health. It can be found in foods such as oysters, nuts, and seeds. Studies suggest that zinc may be helpful in treating acne and other skin conditions.
- Green tea: This antioxidant-rich tea contains compounds that may have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Studies suggest that green tea may help prevent skin damage from UV radiation and improve skin health.
While some nutraceuticals may show promise in treating and preventing skin diseases, it is important to note that they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended before using any nutraceuticals for skin health.
Skin care products available in market
There are a wide variety of skin care products available in the market, each designed to address different skin concerns and needs. Here are some common types of skin care products:

- Cleansers: These are products used to cleanse the skin, removing dirt, oil, and makeup. They come in a variety of forms, such as foaming cleansers, cream cleansers, and cleansing oils.
- Toners: These products are used after cleansing to help remove any remaining impurities and to balance the skin’s pH level. They can come in liquid or mist form.
- These are products used to hydrate the skin, helping to maintain its moisture barrier. They come in a variety of forms, such as creams, lotions, and gels.
- Sunscreens: These products are used to protect the skin from the harmful effects of the sun’s UV rays. They come in different forms, such as lotions, sprays, and sticks.
- Serums: These are concentrated products that contain active ingredients designed to target specific skin concerns, such as fine lines and wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, and acne.
- Exfoliants: These products are used to remove dead skin cells, helping to brighten the skin and improve its texture. They come in physical forms, such as scrubs, and chemical forms, such as AHAs and BHAs.
- Masks: These are products used to provide an extra boost of hydration, to help calm the skin, or to provide other benefits, such as brightening or firming. They come in a variety of forms, such as sheet masks, clay masks, and overnight masks.
It is important to choose skin care products that are appropriate for your skin type and concerns, and to patch test new products before applying them all over your face to ensure you do not have an adverse reaction. Additionally, it is important to establish a consistent skin care routine to see optimal results from the use of these products.
